What is Generative AI Vs AI?
7 min read
Generative AI vs. AI: Understanding the Creative Spark
The world of Artificial Intelligence (AI) is vast and ever-evolving. Within this landscape, a particularly exciting area has captured the imagination of many: Generative AI. But how does it differ from the broader concept of AI, and why is it generating so much buzz?
Understanding AI: The Foundation
Before diving into the specifics of generative AI, let’s establish a basic understanding of AI itself. AI refers to the ability of machines to simulate human intelligence processes, including learning, problem-solving, and decision-making. Various techniques power AI, with machine learning and deep learning at the forefront.
Machine learning involves algorithms that learn from data without explicit programming. Think of it as teaching a computer to recognize patterns and make predictions based on past examples. Deep learning, a subset of machine learning, utilizes artificial neural networks inspired by the human brain to process information and learn complex patterns.
AI in Everyday Life
From voice assistants like Siri and Alexa to recommendation algorithms on streaming platforms, AI is seamlessly integrated into our daily lives. It powers everything from autonomous vehicles to personalized advertising, shaping the way we interact with technology.
Generative AI: Unleashing Creativity
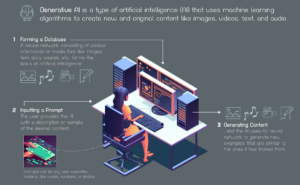
Generative AI, on the other hand, takes AI a step further by focusing on creativity and imagination. While traditional AI systems are designed for specific tasks, Generative AI has the ability to generate new content autonomously.
Generative AI takes a step further, focusing on creating new content rather than simply analyzing or acting on existing data. It leverages the power of deep learning to produce various outputs, including:
- Text: Generative AI can write different kinds of creative text formats, like poems, code, scripts, musical pieces, emails, letters, etc. Examples include tools like ChatGPT and Bard, which can generate human-quality text in response to prompts or questions.
- Images: Imagine describing a fantastical scene and having an AI paint it for you. Tools like DALL-E 2 enable users to generate images from textual descriptions, pushing the boundaries of creative expression.
- Audio: Generative AI can compose music, create realistic sound effects, or even mimic voices. This technology has applications in music production, video game development, and accessibility tools.
- Video: While still in the early stages, generative AI is being explored for video generation, allowing for the creation of new video content from scratch or manipulation of existing footage.
The Creative Force Behind Generative AI
Imagine an artist with a blank canvas, poised to create a masterpiece. Generative AI functions similarly, but instead of paint and brush strokes, it utilizes algorithms and data to generate original content. Whether it’s generating artwork, music, or even text, Generative AI pushes the boundaries of creativity.
The Key Differences: AI vs Generative AI
Now that we have a basic understanding of both concepts, let’s highlight the key differences between AI and Generative AI.
Task-Oriented vs Creative Output
AI is task-oriented, focusing on performing specific tasks efficiently. It excels at tasks like data analysis, natural language processing, and image recognition.
Generative AI, on the other hand, is geared towards producing creative output. It thrives in scenarios where creativity and originality are paramount, such as generating art, music, and literature.
Data Dependency
While both AI and Generative AI rely on data for training, they differ in how they utilize this data. AI typically requires large datasets to learn patterns and make predictions within a given domain.
Generative AI, however, can generate new content based on a relatively small dataset. By leveraging techniques like generative adversarial networks (GANs) and reinforcement learning, it can create diverse and original content with minimal input.

Applications in the Real World
Now that we understand the distinctions between AI and Generative AI, let’s explore their real-world applications.
AI Applications
AI finds applications in various fields, including healthcare, finance, transportation, and entertainment. From diagnosing diseases to optimizing supply chains, AI-driven solutions are revolutionizing industries worldwide.
Generative AI Applications
Generative AI is making waves in creative industries such as art, music, and storytelling. It enables artists to explore new artistic styles, composers to generate unique melodies, and writers to create immersive narratives.
Ethical Considerations: The Future of AI
As we harness the power of AI and Generative AI, it’s crucial to address the ethical implications associated with these technologies.
Bias and Fairness
AI systems are susceptible to biases present in the data used for training. It’s essential to mitigate these biases to ensure fairness and equity in AI-driven decision-making processes.
Creativity and Ownership
With Generative AI blurring the lines between human and machine creativity, questions of ownership and intellectual property rights arise. Who owns the content generated by AI systems, and how do we attribute creativity in a collaborative environment?
The Power of Generative AI: Applications Across Industries
The potential applications of generative AI are vast and span numerous industries:
- Art & Design: Artists and designers can use generative AI tools to explore new creative avenues, generate variations of existing work, or even create entirely new pieces.
- Marketing & Advertising: Generate engaging marketing copy, design captivating visuals, and personalize content for target audiences.
- Entertainment: Create immersive gaming experiences, compose original music, and develop innovative storytelling formats.
- Education: Develop personalized learning tools, generate interactive educational content, and assist with language translation.
- Research & Development: Accelerate scientific discovery by simulating complex systems and generating hypothetical scenarios.
The Ethical Considerations: Navigating the Challenges
As with any powerful technology, generative AI raises ethical considerations that need to be addressed:
- Bias and Fairness: AI models trained on biased data can perpetuate and even amplify existing societal biases. Ensuring fairness and inclusivity in generative AI is crucial.
- Misinformation and Deepfakes: The ability to generate realistic but fabricated content poses a risk of spreading misinformation and creating deepfakes that can be used for malicious purposes.
- Intellectual Property: Questions surrounding copyright and ownership of AI-generated content need to be addressed to protect creators and ensure responsible use of the technology.
The Future of Generative AI: A World of Possibilities
Despite the challenges, generative AI represents a significant leap forward in AI development. As technology continues to evolve and mature, we can expect to see even more innovative applications emerge, transforming industries and pushing the boundaries of human creativity.
The key takeaway: Generative AI isn’t just about mimicking human intelligence; it’s about augmenting it, opening doors to new forms of expression and problem-solving. As we navigate the ethical considerations and harness its power responsibly, generative AI holds the potential to reshape our world in profound ways.
FAQs
Will generative AI replace human artists and creators?
Generative AI is a tool that can augment human creativity, not replace it. While AI can generate impressive outputs, it lacks the human touch, emotional depth, and critical thinking skills that are essential for true artistic expression.
Can I use generative AI to create content for my business?
Absolutely! Generative AI can be a valuable asset for creating marketing materials, product descriptions, and even personalized content for your customers. However, it's crucial to maintain human oversight and ensure the content aligns with your brand values and messaging.
Is generative AI the same as artificial general intelligence (AGI)?
No. Generative AI is a specific type of AI that focuses on creating new content, while AGI refers to a hypothetical AI that possesses human-level intelligence across a wide range of tasks.
How can I ensure the ethical use of generative AI?
Be mindful of potential biases in the data used to train AI models, and use generative AI responsibly to avoid creating harmful content. Always credit AI-generated content transparently and respect intellectual property rights.
What are the limitations of generative AI?
Generative AI models can sometimes produce outputs that are factually incorrect, nonsensical, or biased. It's important to remember that AI is a tool, and its effectiveness depends on the quality of the data it's trained on and the way it's used.
How will generative AI impact the future of work?
Generative AI has the potential to automate certain tasks, particularly in creative fields. However, it will also create new jobs in areas such as AI development, training, and oversight. The key is to adapt and learn new skills to work alongside AI effectively.
Can I use generative AI to create art that I can sell?
The ownership and copyright of AI-generated art are complex issues with evolving legal frameworks. It's essential to research and understand the legalities involved before selling AI-generated art.





